
- #Suse create boot partition install
- #Suse create boot partition update
- #Suse create boot partition free
- #Suse create boot partition windows
#Suse create boot partition windows
The Windows system itself is always located in C.
#Suse create boot partition install
It is often necessary - especially when one wants to install several operating systems on the same computer - to divide the hard disk into several regions and to attribute every one of them to such or such operating system. This type of formatting is also known as low-level formatting. This is done to interface with the controller's hardware and firmware. That means that damaged tracks are marked and replacements used, sector numbers are written. The operating systems can not see if a disk is inside the system enclosure, beside it, on a table, or on another shelf, so there is no difference between what some people call internal and external disks.ĭisks are normally supplied formatted by the manufacturer. No matter whether it is a flash device that looks like a disk, an optical drive or a 'real' hard disk, or even a combination of several devices.īecause newer types of mass storage devices present themselves to the system as disks, they fall into this category. a place where they can store and retrieve data perennially - perennially implying the idea of nonvolatility when powering the computer off. In this document, the word disk will be used as a generic term for anything that is seen by operating systems as a disk drive i.e.

4.1 Description of the Linux Filesystem.

4 The Linux Filesystem and its Setting Up.3.2.1 GPT Partitioning and Booting with a UEFI Firmware.3.1.2 Primary, Extended and Logical Partitions.I recommend storing /boot/ on a shared partition and using a raid.
#Suse create boot partition free
If there is free space left on the disk, you can partition it to fit your needs using fdisk and mkfs.ext4. We change disks in places, that is we connect a new disk first that it became /dev/sdа, we include the server, the system should boot through the loader on the first section. Now you can turn off the server: sudo poweroff

#Suse create boot partition update
Update the GRUB: sudo grub-install /dev/sdb Mount the new partition in /boot/: sudo umount /mnt/ We will specify it in the file /etc/fstab for automatic mounting: sudo nano /etc/fstab Let’s see the UUID of the new partition with /boot/: lsblk -o NAME,UUID Make sure that the data is copied and clean the /boot/ folder on the main partition: sudo ls -l /mnt We copy the data /boot/ from the shared partition to a separate partition: sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/ Make the partition active: sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
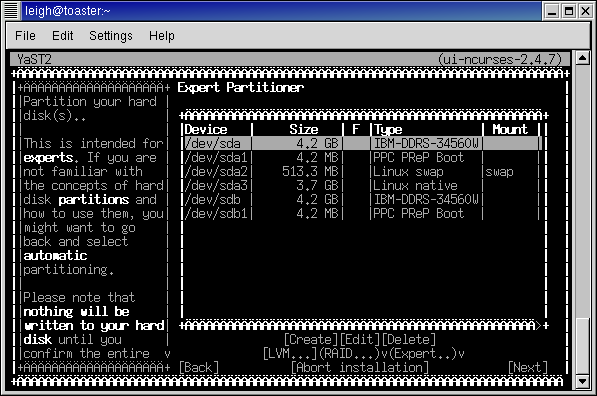
Suppose we have connected a new unmapped disk /dev/sdb, we create on it the first partition for boot with a size of 512 MB: sudo fdisk /dev/sdbĬreate an ext2 table: sudo mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdb1


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
